C++ Basic Course
Chapter 1——Hello, C++!
WHY C++?
Popular
As a qualified programmer, you should know how to chase trends!
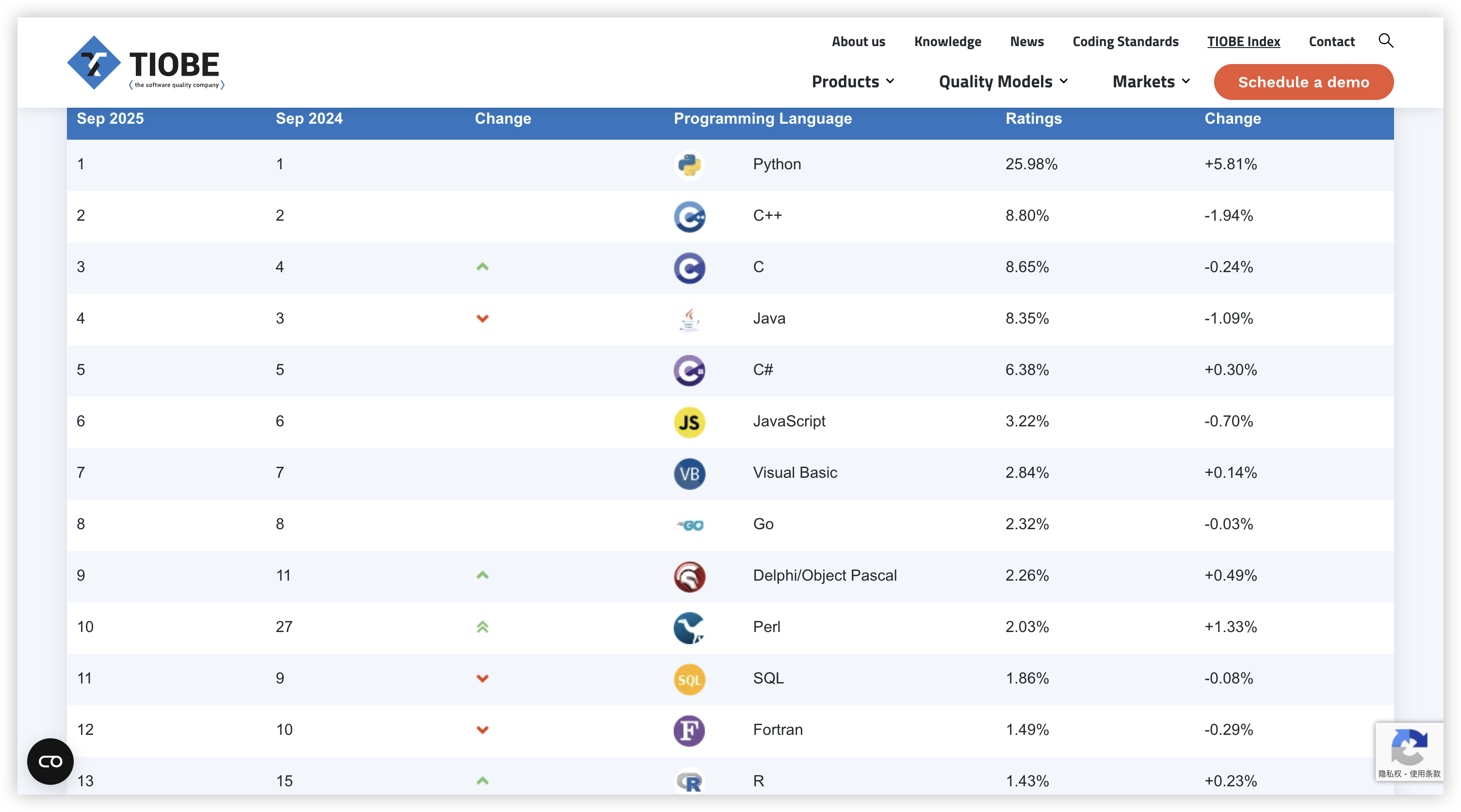
Fast && Lower level control
C++ is fast, including but not limited to
- its static type system, which reduces runtime overhead
- and its ability to allow direct memory access and management, thereby reducing additional runtime costs.
What is C++?
This is some C++ code
1 2 3 4 5 6#include <iostream> int main() { std::cout << "Hello, world!" << std::endl; return 0; }This is also some C++ code! (code style before C99)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7#include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" int main(int argc, char *argv) { printf("%s" "Hello, world!\n"); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }Also technically C++ code!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17#include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" int main(int argc, char *argv) { asm( "sub $0x20,%rsp\n\t" "movabs $0x77202c6f6c6c6548,%rax\n\t" "mov %rax,(%rsp)\n\t" "movl $0x646c726f, 0x8(%rsp)\n\t" "movw $0x21, 0xc(%rsp)\n\t" "movb $0x0,0xd(%rsp)\n\t" "leaq (%rsp),%rax\n\t" "mov %rax,%rdi\n\t" "call __Z6mtputsPc\n\t" "add $0x20, %rsp\n\t" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }Code is getting longer and older
All that means C++ is backwards compatible with lower level languages! And neat!
C++ History: Assembly
Observe the following assembly code, make a guess about its purpose, and note any distinctive features of the code.
| |
Benefits:
- Unbelievable simple instructions
- Extremely fast (when well-written)
- Complete control over your program
Why don’t we always use assembly?
Drawbacks:
- A LOT of code to do simple tasks
- Very hard to understand
- Extremely unportable (hard to make work across all systems)
C++ History: invention of C
Problem: computers can only understand assembly!
Idea:
- Source code can be written in a more intuitive language for humans.
- An additional program can convert it into assembly!
- This additional program is called a compiler!
Based on the above concepts, Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie created C in 1972, to much praise.

C made it easy to write code that was:
- Fast
- Simple
- Cross-platform
C was popular because it was simple, this was also its weakness:
- No Objects or classes
- Difficult to write generic code
- Tedious when writing large programs
C++ History: Welcome to C++
In 1983, the beginnings of C++ were created by Bjarne Stroustrup.

He wanted a language that was:
- Fast
- Simple to use
- Cross-platform
- Had high-level features
C++ History: Evolution of C++
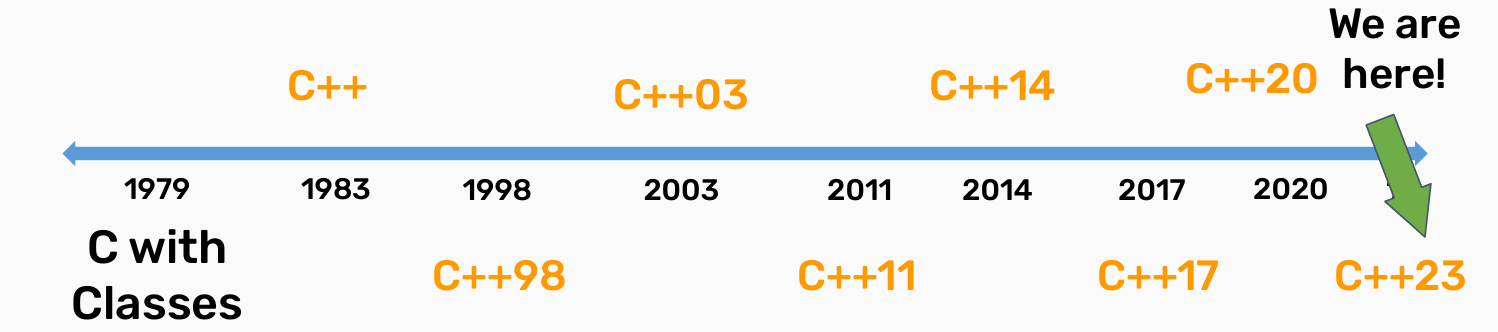
Design Philosophy of C++
- Only add features if they solve an actual problem
- This principle emphasizes that new language features should be added to address real-world programming problems rather than introducing complexity for its own sake. It helps maintain the simplicity and maintainability of the language.
- Programmers should be free to choose their own style
- C++ provides multiple programming paradigms (such as procedural, object-oriented, and generic programming) and doesn’t impose a specific coding style. This allows programmers to write code according to their own needs and preferences.
- Not code style
- Compartmentalization is key
- This means that programs should be broken down into small, independent modules, each responsible for specific tasks. Modular code is easier to maintain, test, and reuse.
- Allow the programmer full control if they want it
- C++ offers low-level memory access and operations to satisfy the needs of programmers who require a higher degree of control. This is valuable for system programming and performance optimization.
- Don’t sacrifice performance except as a last resort
- C++ places a high priority on performance and encourages programmers to write efficient code. Performance should only be sacrificed when there are no other alternatives.
- Enforce safety at compile time whenever possible
- C++ strives to catch and prevent common programming errors, such as type errors and null pointer references, at compile time. This reduces runtime errors, enhancing code quality and reliability.
But… Back to that question: what is C++?
See you tomorrow!